Securing Passwords⚓︎
Summary⚓︎
Passwords are something that virtually everyone has to deal with sooner or later. The problem is that most people don't have a good grasp on good password hygeine or even the basics of security. It's important to note that most people do, however, understand the nature of security risks related to easy-to-guess passwords. In creating passwords for various websites and services, there is typically a password policy (1) guiding what a user can or can't use for a password. What ends up happening though is that because passwords are inherently difficult to remember, they often get reused for the sake of making it easier to remember.
- Password policies are a set of rules created to increase password security by encouraging users to create strong, secure passwords, and then store and utilize them properly.
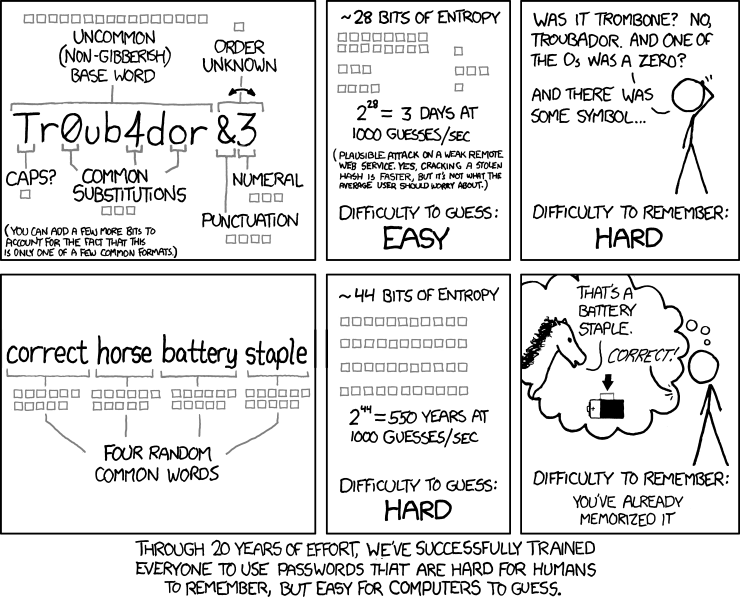
For good reason, one of the most popular images when it comes to remembering passwords is the following from XKCD...
It perfectly illustrates the difficulties associated with passwords and remembering them. Since people are inherently not good at remembering passwords and passwords are not going anywhere, what can be done?
This article will be a guide on modern password security policies and best practices. 1
Principles of Password Management⚓︎
Create A Strong, Long Passphrase⚓︎
Strong passwords make it significantly more difficult for hackers to crack and break into systems. Strong passwords are considered over eight characters in length and made up of both upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends creating long passphrases that are easy to remember and difficult to crack. According to Special Publication 800-63, Digital Identity Guidelines, a best practice is to generate passwords of up to 64 characters, including spaces.
Implement Two-Factor Authentication⚓︎
Two-factor authentication has fast become a standard for managing access to organizational resources. In addition to traditional credentials like username and password, users have to confirm their identity with a one-time code sent to their mobile device or using a personalized USB token. The idea is that with two-factor (or multi-factor) authentication, guessing or cracking the password alone is not enough for an attacker to gain access.
Test Your Password⚓︎
Make sure your password is strong by testing it with an online testing tool. Microsoft’s Safety & Security Center has a password testing tool that can help you generate passwords that are less likely to be hacked. 2
Don’t Use Dictionary Words⚓︎
Sophisticated hackers have programs that search through tens of thousands of dictionary words. Avoid dictionary words to help prevent your business from being a victim of a dictionary attack program.
Use Different Passwords for Every Account⚓︎
Otherwise, if one account is breached, other accounts with the same credentials can easily by compromised
Avoid Storing Passwords⚓︎
Avoid storing passwords either digitally or on paper, as this information can be stolen by those with malicious motives.
Use Password Managers⚓︎
By leveraging a password manager, you only need to remember one password, as the password manager stores and even creates passwords for your different accounts, automatically signing you in when you log on.
View a password manager as a book of your passwords, locked by a master key that only you know. Some of you think that sounds bad because, if someone acquires the master password, they have ALL your passwords. But if you’ve chosen a strong and unique, but easy-to-remember master password—you’ve established a near-perfect way to protect the rest of your personal passwords from improper access.
Password managers not only store your passwords, they help you generate and save strong, unique passwords when you sign up to new websites. That means whenever you go to a website or app, you can pull up your password manager, copy your password, paste it into the login box, and you’re in. Often, password managers come with browser extensions that automatically fill in your password for you.
And because many of the password managers in use have encrypted sync across devices, you can take your passwords with you anywhere — even on your phone.
Password managers are designed to provide you with access to all of your passwords in an encrypted format that is not accessible to hackers or malicious software. They can offer significant convenience while providing outstanding protection and ensuring that your information stays private.
References⚓︎
https://www.beyondtrust.com/blog/entry/top-15-password-management-best-practices
-
The content of this guide will largely be taken from the BeyondTrust blog as the advice provided is second to none. ↩
-
There are other password tools that can be utilized as well. One of the best is from Bitwarden, which makes use of zxcvbn, a password strength estimator. ↩